Uttamenergy has commissioned 3750 TCD, 12.5 MW Integrated Sugar Plant in Parner, Maharashtra!
/in Latest News, News/by Uttamenergy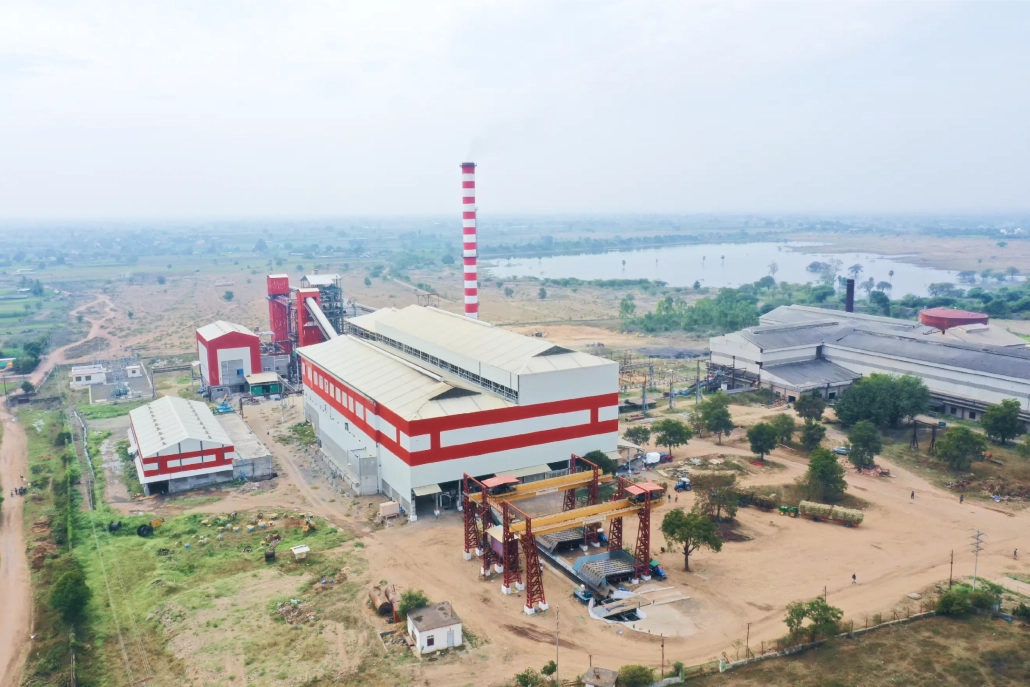
This power plant includes a high efficient 70 TPH, 73 kg/cm2(g), 515°C Integrated Sugar Plant capable of Handling Bagasse fuel.
This not only ensures eco-friendliness but also results in significant emission reduction.
💪 Delivering clean energy solutions for a sustainable future 💡
Uttamenergy Powers Up 25 MW Co-Generation Plant in Belgavi, Karnataka!
/in Latest News, News/by Uttamenergy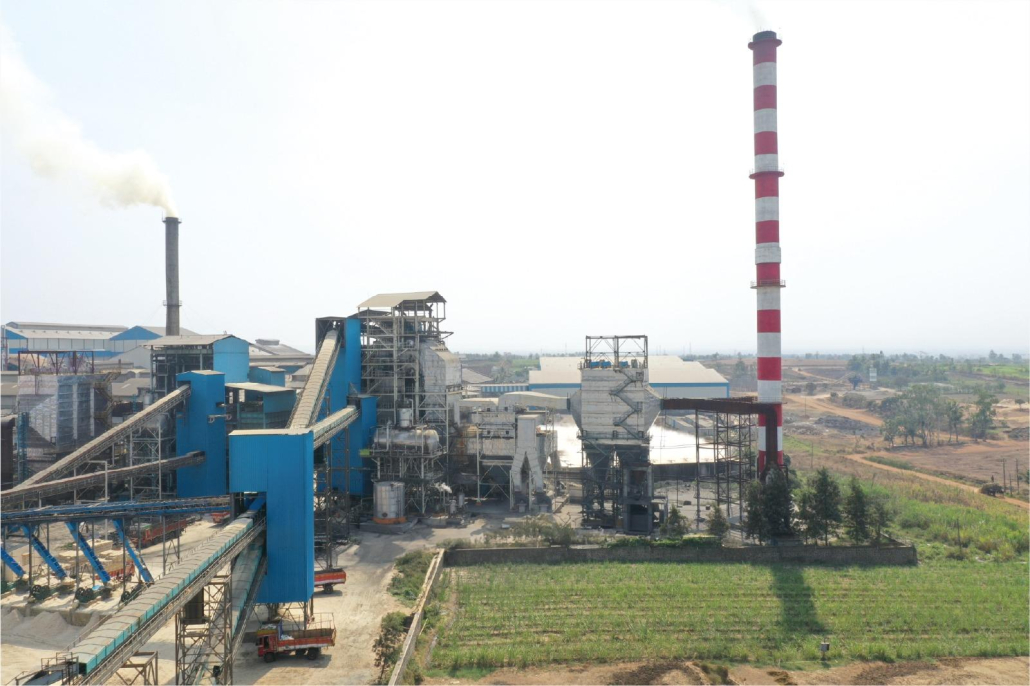
This power plant includes a high efficient 140 TPH, 73 kg/cm2(g), 510°C Travelling Grate Boiler capable of Handling Bagasse fuel.
This not only ensures eco-friendliness but also results in significant emission reduction.
💪 Delivering clean energy solutions for a sustainable future 💡
Uttamenergy Powers Up 3.5 MW Co-Generation Plant in Bagodara, Gujarat!
/in Latest News, News/by Uttamenergy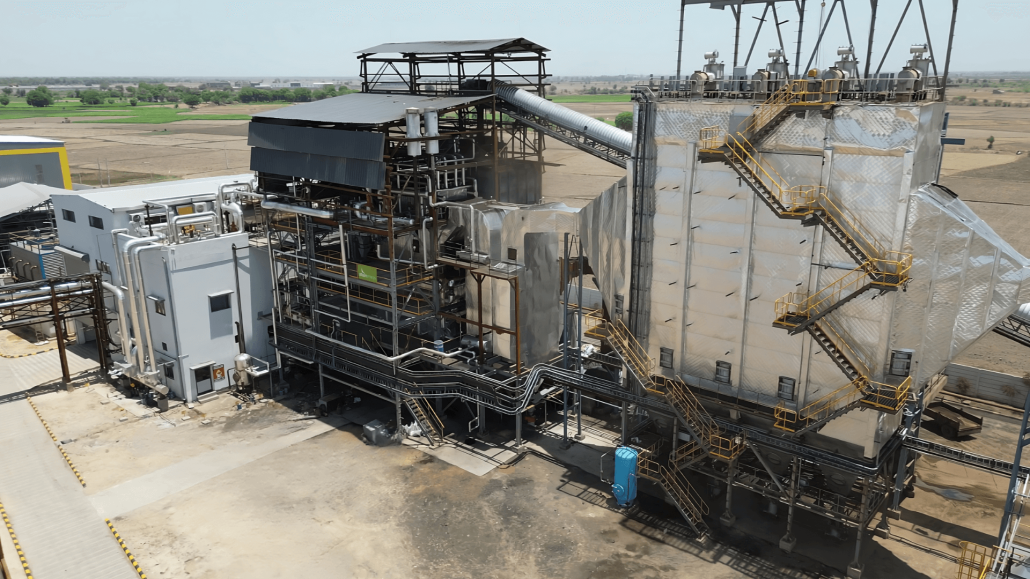
This power plant includes a high efficient 1 x 30 TPH, 67 kg/cm2(g), 490°C AFBC Boiler capable of handling Rice Husk & coal fuels.
This not only ensures eco-friendliness but also results in significant emission reduction.
Our dedicated powerplant solution is wholly focused on meeting the steam and power needs of the client’s 100 KLPD Grain-Based Distillery.
💪 Delivering clean energy solutions for a sustainable future 💡
Uttamenergy Powers Up 3.35 MW Co-Generation Plant in Athani, Karnataka!
/in Latest News, News/by Uttamenergy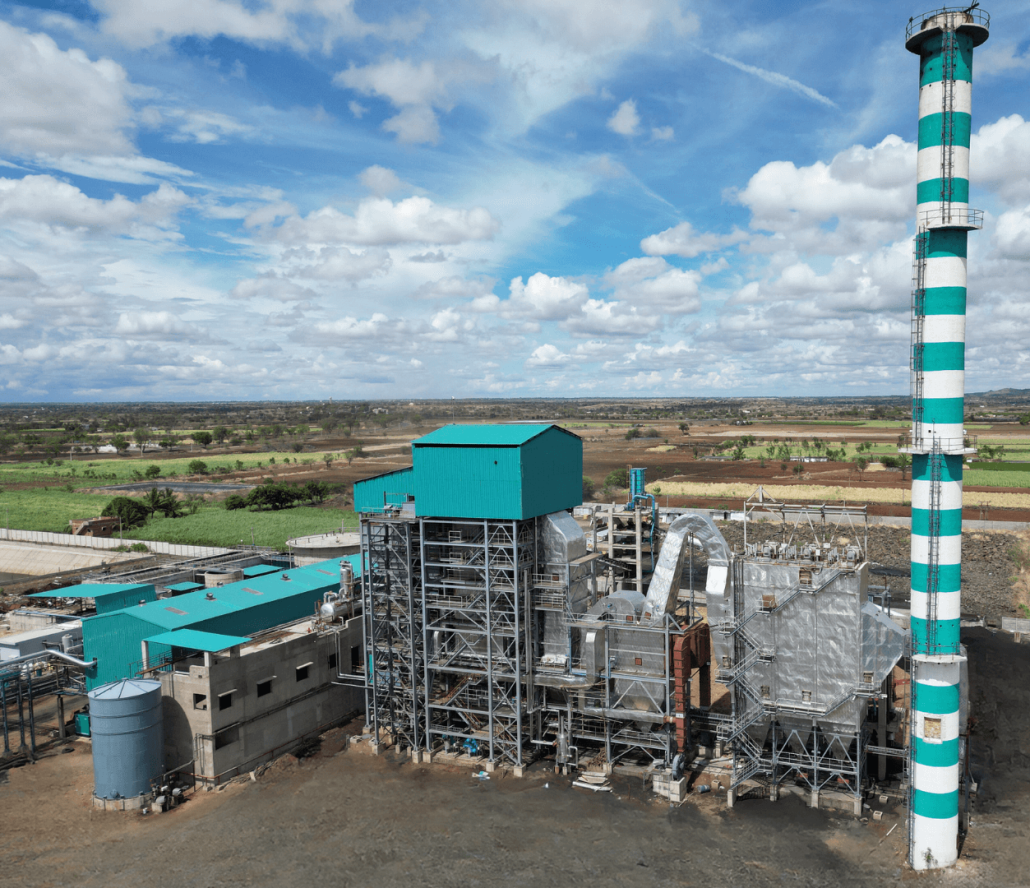
This power plant includes a high efficient 32 TPH, 45 kg/cm2(g), 490°C Travelling Grate Boiler capable of handling multiple biomass fuels.
This not only ensures eco-friendliness but also results in significant emission reduction.
Our dedicated powerplant solution is wholly focused on meeting the steam and power needs of the client’s 100 KLPD Grain-Based Distillery.
💪 Delivering clean energy solutions for a sustainable future 💡
Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Waste to Energy Technologies
/in Blog/by WebleadsAs we confront the global challenges of waste management and environmental sustainability, innovative solutions like waste-to-energy technologies offer promising alternatives.
These technologies transfigure waste materials into valuable energy sources, simultaneously reducing waste volume and mollifying environmental impacts. In this comprehensive blog, we will delve into the benefits and challenges of waste- to- energy technologies, shedding light on their implicit and limitations.
Exploring the Benefits and Challenges of Waste to Energy Technologies
What’s Waste- to- Energy?
Waste-to-energy refers to the conversion of waste materials into usable energy. This involves various processes like anaerobic digestion, gasification, pyrolysis, and incineration.
Benefits of Waste- to- Energy Technologies:
1. Renewable Energy Generation:
One of the primary benefits of waste- to- energy technologies are the generation of renewable energy. By employing the energy content of waste materials, these technologies give a sustainable volition to reactionary energy- grounded energy sources.
The produced energy can power homes, businesses, and indeed contribute to the original energy grid, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
2. Waste Volume Reduction:
Waste-to- energy solutions effectively reduce the volume of waste that would else be transferred to dumps. This not only saves valuable land resources but also minimizes the release of dangerous pollutants and greenhouse gases associated with landfilling.
3. Mitigation of Greenhouse Gas Emissions:
By carrying methane and other greenhouse gases released from waste decomposition, waste- to- energy technologies contribute to climate change mitigation.
Methane, a potent greenhouse gas, is combusted or converted into usable energy during the waste- to- energy process, thereby preventing its release into the atmosphere.
4. Resource Recovery:
Waste- to- energy technologies enable the recovery of valuable resources from waste channels. Metals, glass, and plastics can be extracted, recycled, and reused, reducing the need for virgin materials and promoting a circular economy.
Challenges and Limitations of Waste to Energy Technologies
1 Environmental Concerns:
While waste- to- energy technologies offer multiple environmental benefits, there are enterprises regarding air emissions, including pollutants like particulate matter, nitrogen oxides,dioxins. Still, advancements in emission control technologies help alleviate these concerns, ensuring compliance with stringent air quality norms.
2 Economic Viability:
Implementing waste-to-energy technologies requires substantial investments in infrastructure and operational costs. Assessing the economic viability of such projects and developing sustainable financing models are critical challenges that need to be addressed.
3 Public Perception and Engagement:
Engaging the public and addressing misconceptions about waste-to-energy technologies is crucial for their successful implementation. Clear communication and community involvement are vital to gain public acceptance and support for these initiatives.
4 Feedstock Availability and Composition:
The availability and composition of waste feedstock pose challenges to waste-to-energy technologies. Variations in waste composition can affect the efficiency and performance of these processes. Adequate waste segregation, recycling, and waste management practices are essential to optimize the feedstock quality.
Conclusion:
Waste-to-energy technologies hold tremendous potential in addressing waste management challenges and driving a transition towards a sustainable future.
The benefits of renewable energy generation, waste volume reduction, greenhouse gas mitigation, and resource recovery make these technologies invaluable in our quest for environmental sustainability.
However, challenges related to environmental concerns, economic viability, public perception, and feedstock availability must be addressed through continued research, innovation, and stakeholder collaboration.
It’s essential that we adopt waste-to- energy technologies in a responsible manner going forward, making sure there are strong regulatory frameworks, effective emission control tactics, and community involvement.
We can all work together to produce a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable atmosphere for future generations by utilizing the eventuality of waste- to- energy technology and enforcing comprehensive waste management plans.
About Us
Uttamenergy is in the business of providing EPC solutions for power plants with high efficiency steam boilers.
Latest News
 The Biofuel Exhibition10 June 2024 - 2:54 pm
The Biofuel Exhibition10 June 2024 - 2:54 pm Annual Africa Sugar Conference02 May 2024 - 3:32 pm
Annual Africa Sugar Conference02 May 2024 - 3:32 pm Uttamenergy has commissioned 3750 TCD, 12.5 MW Integrated Sugar Plant in Parner, Maharashtra!22 April 2024 - 11:23 am
Uttamenergy has commissioned 3750 TCD, 12.5 MW Integrated Sugar Plant in Parner, Maharashtra!22 April 2024 - 11:23 am Uttamenergy Powers Up 25 MW Co-Generation Plant in Belgavi, Karnataka!22 April 2024 - 11:08 am
Uttamenergy Powers Up 25 MW Co-Generation Plant in Belgavi, Karnataka!22 April 2024 - 11:08 am Uttamenergy Powers Up 3.5 MW Co-Generation Plant in Bagodara, Gujarat!27 March 2024 - 12:16 pm
Uttamenergy Powers Up 3.5 MW Co-Generation Plant in Bagodara, Gujarat!27 March 2024 - 12:16 pm
Contact Us
Uttamenergy Limited,
7th floor, Business Plaza,
The Westin, Mundhwa Rd, Koregaon Park Annexe, Ghorpadi, Pune – 411001,
Maharashtra, India.
Email: contact@uttamenergy.com







